class Solution {
public:
bool isSubsetSum(vector<int>& arr, int sum) {
vector<vector<int>> memo(arr.size()+1, vector<int>(sum+1, -1));
function<bool(vector<int>&, int, int)> dp = [&](vector<int>& ar, int index, int sum){
if( sum == 0 ) return true;
if( index == 0 ) return false;
if( memo[index][sum] != -1 )
return memo[index][sum]==1;
bool result = dp(ar, index-1, sum );
if( ar[index-1] <= sum )
result = result || dp(ar, index-1, sum - ar[index-1]);
memo[index][sum] = result;
return result ;
};
return dp(arr, arr.size(), sum);
}
};
Tag: c++
2206. Divide Array Into Equal Pairs
class Solution {
public:
bool divideArray(vector<int>& nums) {
int ar[501];
for( int num:nums){
ar[num]++;
}
for( int element : ar ){
if( element%2 != 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
};
C++ Solution for LeetCode 2594. Minimum Time to Repair Cars
long long repairCars(vector<int>& ranks, int cars) {
//long long min_r = *min_element(ranks.begin(), ranks.end());
long long left = 1;
long long right = ranks[0] * (long long)cars * cars;
long long result = right; // Initialize with an upper bound
auto countRepairCars = [&ranks](long long time) {
long long repaired = 0;
for (int r : ranks) {
repaired += (long long)sqrt((double)time / r);
}
return repaired;
};
while (left <= right) {
long long midpoint = left + (right - left) / 2;
long long repaired = countRepairCars(midpoint);
if (repaired >= cars) {
result = midpoint; // Found a valid time, try to minimize it
right = midpoint - 1;
} else {
left = midpoint + 1;
}
}
return result;
}
2467. Most Profitable Path in a Tree
There is an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, rooted at node 0. You are given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1 where edges[i] = [a<sub>i</sub>, b<sub>i</sub>] indicates that there is an edge between nodes a<sub>i</sub> and b<sub>i</sub> in the tree.
At every node i, there is a gate. You are also given an array of even integers amount, where amount[i] represents:
- the price needed to open the gate at node
i, ifamount[i]is negative, or, - the cash reward obtained on opening the gate at node
i, otherwise.
The game goes on as follows:
- Initially, Alice is at node
0and Bob is at nodebob. - At every second, Alice and Bob each move to an adjacent node. Alice moves towards some leaf node, while Bob moves towards node
0. - For every node along their path, Alice and Bob either spend money to open the gate at that node, or accept the reward. Note that:
- If the gate is already open, no price will be required, nor will there be any cash reward.
- If Alice and Bob reach the node simultaneously, they share the price/reward for opening the gate there. In other words, if the price to open the gate is
c, then both Alice and Bob payc / 2each. Similarly, if the reward at the gate isc, both of them receivec / 2each.
- If Alice reaches a leaf node, she stops moving. Similarly, if Bob reaches node
0, he stops moving. Note that these events are independent of each other.
Return the maximum net income Alice can have if she travels towards the optimal leaf node.
Example 1: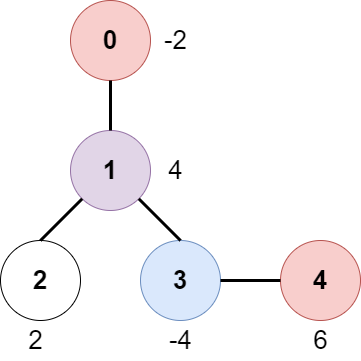
Input: edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3],[3,4]], bob = 3, amount = [-2,4,2,-4,6] Output: 6 Explanation: The above diagram represents the given tree. The game goes as follows: - Alice is initially on node 0, Bob on node 3. They open the gates of their respective nodes. Alice's net income is now -2. - Both Alice and Bob move to node 1. Since they reach here simultaneously, they open the gate together and share the reward. Alice's net income becomes -2 + (4 / 2) = 0. - Alice moves on to node 3. Since Bob already opened its gate, Alice's income remains unchanged. Bob moves on to node 0, and stops moving. - Alice moves on to node 4 and opens the gate there. Her net income becomes 0 + 6 = 6. Now, neither Alice nor Bob can make any further moves, and the game ends. It is not possible for Alice to get a higher net income.
Example 2:
Input: edges = [[0,1]], bob = 1, amount = [-7280,2350] Output: -7280 Explanation: Alice follows the path 0->1 whereas Bob follows the path 1->0. Thus, Alice opens the gate at node 0 only. Hence, her net income is -7280.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 10<sup>5</sup>edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= a<sub>i</sub>, b<sub>i</sub> < na<sub>i</sub> != b<sub>i</sub>edgesrepresents a valid tree.1 <= bob < namount.length == namount[i]is an even integer in the range[-10<sup>4</sup>, 10<sup>4</sup>].
#include <vector>
#include <climits>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int mostProfitablePath(vector<vector<int>>& edges, int bob, vector<int>& amount) {
int n = amount.size();
// Build adjacency list
vector<vector<int>> graph(n);
for (auto& edge : edges) {
graph[edge[0]].push_back(edge[1]);
graph[edge[1]].push_back(edge[0]);
}
// Find Bob's path to root
vector<int> bobPath;
vector<bool> visited(n, false);
findPath(graph, bob, 0, visited, bobPath);
// Set Bob's visitation times
vector<int> bobTime(n, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < bobPath.size(); i++) {
bobTime[bobPath[i]] = i;
}
// Reset visited and run DFS for Alice
visited.assign(n, false);
return dfs(graph, 0, 0, bobTime, amount, visited);
}
private:
// DFS to find path from start to target
bool findPath(vector<vector<int>>& graph, int start, int target,
vector<bool>& visited, vector<int>& path) {
visited[start] = true;
path.push_back(start);
if (start == target) return true;
for (int next : graph[start]) {
if (!visited[next]) {
if (findPath(graph, next, target, visited, path)) {
return true;
}
}
}
path.pop_back();
return false;
}
// DFS to compute Alice's maximum income
int dfs(vector<vector<int>>& graph, int node, int time,
vector<int>& bobTime, vector<int>& amount, vector<bool>& visited) {
visited[node] = true;
// Calculate income at current node
int income;
if (bobTime[node] == -1 || bobTime[node] > time) {
income = amount[node]; // Bob arrives after or never
} else if (bobTime[node] == time) {
income = amount[node] / 2; // Simultaneous arrival
} else {
income = 0; // Bob arrives before
}
// Check if leaf node
bool isLeaf = true;
for (int next : graph[node]) {
if (!visited[next]) {
isLeaf = false;
break;
}
}
if (isLeaf) {
return income;
}
// Explore children and find maximum path income
int maxChildIncome = INT_MIN;
for (int next : graph[node]) {
if (!visited[next]) {
int childIncome = dfs(graph, next, time + 1, bobTime, amount, visited);
maxChildIncome = max(maxChildIncome, childIncome);
}
}
// If no children were explored (shouldn't happen in a valid tree from root),
// but handle it safely
if (maxChildIncome == INT_MIN) {
return income; // Should not occur as root has children
}
return income + maxChildIncome;
}
};
Binary Search —- AGAIN!
int binarySearch(vector<int> &nums, int target) {
int low =0, high = nums.size()-1;
while( low <= high ){
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if( nums[mid] == target )
return mid;
else if( nums[mid] < target )
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid -1;
}
return -1;
}
Parenthesis Checker
Given a string s, composed of different combinations of ‘(‘ , ‘)’, ‘{‘, ‘}’, ‘[‘, ‘]’, verify the validity of the arrangement.
An input string is valid if:
1. Open brackets must be closed by the same type of brackets.
2. Open brackets must be closed in the correct order.
Examples :
Input: s = "[{()}]"
Output: true
Explanation: All the brackets are well-formed.
Input: s = "[()()]{}"
Output: true
Explanation: All the brackets are well-formed.
Input: s = "([]"
Output: False
Explanation: The expression is not balanced as there is a missing ')' at the end.
Input: s = "([{]})"
Output: False
Explanation: The expression is not balanced as there is a closing ']' before the closing '}'.
Constraints:
1 ≤ s.size() ≤ 106
s[i] ∈ {‘{‘, ‘}’, ‘(‘, ‘)’, ‘[‘, ‘]’}
class Solution {
public:
bool isBalanced(string& s) {
stack<char> st;
unordered_map<char,char> mp = {
{'{','}'},
{'(',')'},
{'[',']'}
};
for( char c:s ) {
if( mp.count(c) )
st.push(c);
else {
if( st.empty() || mp[st.top()] != c )
return false;
st.pop();
}
}
return st.empty();
}
};
Stock Span
The stock span problem is a financial problem where we have a series of daily price quotes for a stock and we need to calculate the span of stock price for all days. The span arr[i] of the stocks price on a given day i is defined as the maximum number of consecutive days just before the given day, for which the price of the stock on the given day is less than or equal to its price on the current day.
Examples:
Input: arr[] = [100, 80, 60, 70, 60, 75, 85] Output: [1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 4, 6] Explanation: Traversing the given input span 100 is greater than equal to 100 and there are no more elements behind it so the span is 1, 80 is greater than equal to 80 and smaller than 100 so the span is 1, 60 is greater than equal to 60 and smaller than 80 so the span is 1, 70 is greater than equal to 60,70 and smaller than 80 so the span is 2 and so on. Hence the output will be 1 1 1 2 1 4 6.
Input: arr[] = [10, 4, 5, 90, 120, 80] Output: [1, 1, 2, 4, 5, 1] Explanation: Traversing the given input span 10 is greater than equal to 10 and there are no more elements behind it so the span is 1, 4 is greater than equal to 4 and smaller than 10 so the span is 1, 5 is greater than equal to 4,5 and smaller than 10 so the span is 2, and so on. Hence the output will be 1 1 2 4 5 1.
Input: arr[] = [11, 4, 5, 90, 120, 80] Output: [1, 1, 2, 4, 5, 1] Explanation: Traversing the given input span 11 is greater than equal to 11 and there are no more elements behind it so the span is 1, 4 is greater than equal to 4 and smaller than 10 so the span is 1, 5 is greater than equal to 4,5 and smaller than 10 so the span is 2, and so on. Hence the output will be 1 1 2 4 5 1.
Constraints:
1 ≤ arr.size()≤ 105
1 ≤ arr[i] ≤ 105
//{ Driver Code Starts
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// } Driver Code Ends
class Solution {
public:
bool isBalanced(string& s) {
// code here
stack<char> st;
unordered_map<char,char> mp;
mp.set('{','}');
mp.set('(',')');
mp.set('[',']');
for( char c:s ){
if( mp[st.top()] == c )
st.pop();
} else
st.push(c);
}
return st.size() == 0;
}
};
//{ Driver Code Starts.
int main() {
int t;
string a;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
cin >> a;
Solution obj;
if (obj.isBalanced(a))
cout << "true" << endl;
else
cout << "false" << endl;
cout << "~"
<< "\n";
}
}
// } Driver Code Ends
Construct the Smallest Number
Developers flex on each with the strangest of ways. How green is your github commit history. Have you submitted a PR to a open source project. How well can you solve the silliest questions on leetcode / geeksforgeeks / hackerrank?
While normies use money and status as a measure of success. Coders have incelled their way into a paradise where the glow of the monitor is all you need.
Pray for death all you want, it’s not coming. Man up and start grinding.
You are given a 0-indexed string pattern of length n consisting of the characters 'I' meaning increasing and 'D' meaning decreasing.
A 0-indexed string num of length n + 1 is created using the following conditions:
numconsists of the digits'1'to'9', where each digit is used at most once.- If
pattern[i] == 'I', thennum[i] < num[i + 1]. - If
pattern[i] == 'D', thennum[i] > num[i + 1].
Return the lexicographically smallest possible string num that meets the conditions.
Example 1:
Input: pattern = "IIIDIDDD" Output: "123549876" Explanation: At indices 0, 1, 2, and 4 we must have that num[i] < num[i+1]. At indices 3, 5, 6, and 7 we must have that num[i] > num[i+1]. Some possible values of num are "245639871", "135749862", and "123849765". It can be proven that "123549876" is the smallest possible num that meets the conditions. Note that "123414321" is not possible because the digit '1' is used more than once.
Example 2:
Input: pattern = "DDD" Output: "4321" Explanation: Some possible values of num are "9876", "7321", and "8742". It can be proven that "4321" is the smallest possible num that meets the conditions.
Constraints:
1 <= pattern.length <= 8patternconsists of only the letters'I'and'D'.
class Solution {
public:
string smallestNumber(string pattern) {
string result;
stack<int> st;
for( int i = 0; i<= pattern.size(); i++ ){
st.push(i+1);
if ( i == pattern.length() || pattern[i] == 'I' )
while(!st.empty()){
result+=to_string( st.top() );
st.pop();
}
}
return result;
}
};
Generating Subsets using Backtracking
1863. Sum of All Subset XOR Totals
This is a good problem to grasp basics of backtracking
The XOR total of an array is defined as the bitwise XOR of all its elements, or 0 if the array is empty.
- For example, the XOR total of the array
[2,5,6]is2 XOR 5 XOR 6 = 1.
Given an array nums, return the sum of all XOR totals for every subset of nums.
Note: Subsets with the same elements should be counted multiple times.
An array a is a subset of an array b if a can be obtained from b by deleting some (possibly zero) elements of b.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,3] Output: 6 Explanation: The 4 subsets of [1,3] are: - The empty subset has an XOR total of 0. - [1] has an XOR total of 1. - [3] has an XOR total of 3. - [1,3] has an XOR total of 1 XOR 3 = 2. 0 + 1 + 3 + 2 = 6
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,1,6] Output: 28 Explanation: The 8 subsets of [5,1,6] are: - The empty subset has an XOR total of 0. - [5] has an XOR total of 5. - [1] has an XOR total of 1. - [6] has an XOR total of 6. - [5,1] has an XOR total of 5 XOR 1 = 4. - [5,6] has an XOR total of 5 XOR 6 = 3. - [1,6] has an XOR total of 1 XOR 6 = 7. - [5,1,6] has an XOR total of 5 XOR 1 XOR 6 = 2. 0 + 5 + 1 + 6 + 4 + 3 + 7 + 2 = 28
Example 3:
Input: nums = [3,4,5,6,7,8] Output: 480 Explanation: The sum of all XOR totals for every subset is 480.
class Solution {
vector<vector<int>> subset;
void backtrack(vector<int> &nums,vector<int> ¤t,int index){
subset.push_back(current);
for(int i = index; i < nums.size(); i++ ){
current.push_back(nums[i]);
backtrack( nums, current, i+1);
current.pop_back();
}
}
public:
int subsetXORSum(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> current;
backtrack(nums,current,0);
int total_sum = 0;
for (const auto& sub : subset) {
int xor_sum = 0;
for (int num : sub) {
//std::cout<<num<<" ";
xor_sum ^= num;
}
//std::cout<<std::endl;
total_sum += xor_sum;
}
return total_sum;
}
};
k largest elements
Given an array arr[] of positive integers and an integer k, Your task is to return k largest elements in decreasing order.
Examples:
Input: arr[] = [12, 5, 787, 1, 23], k = 2 Output: [787, 23] Explanation: 1st largest element in the array is 787 and second largest is 23.
Input: arr[] = [1, 23, 12, 9, 30, 2, 50], k = 3 Output: [50, 30, 23] Explanation: Three Largest elements in the array are 50, 30 and 23.
Input: arr[] = [12, 23], k = 1 Output: [23] Explanation: 1st Largest element in the array is 23.
Constraints:
1 ≤ k ≤ arr.size() ≤ 106
1 ≤ arr[i] ≤ 106
class Solution {
std::vector<int> minHeapToVector(std::priority_queue<int, std::vector<int>, std::greater<int>> minHeap) {
std::vector<int> result;
while (!minHeap.empty()) {
result.push_back(minHeap.top());
minHeap.pop();
}
std::reverse(result.begin(), result.end());
return result;
}
public:
vector<int> kLargest(vector<int>& arr, int k) {
std::priority_queue<int, std::vector<int>, std::greater<int>> minHeap;
for( int i : arr ){
if( minHeap.size() < k )
minHeap.push(i);
else if( minHeap.top()<=i ){
minHeap.pop();
minHeap.push(i);
}
}
return minHeapToVector(minHeap);
}
};
